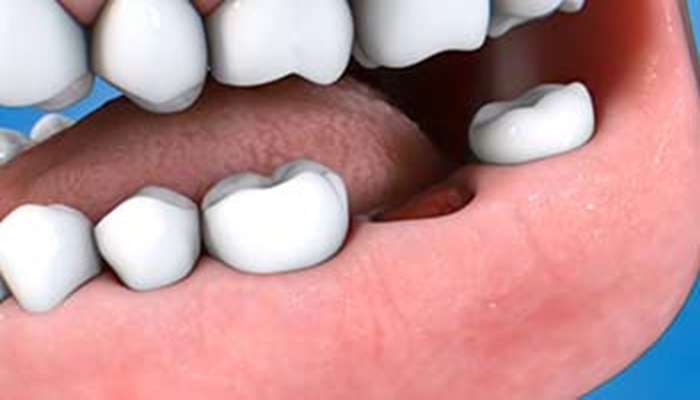
A bone spicule, in dental terms, refers to a small fragment of bone or tooth root that remains embedded in the gum tissue after a tooth extraction or other dental procedure. These spicules can sometimes protrude through the gum, causing discomfort, irritation, and potential complications if left untreated.
When a tooth is extracted, the goal is to remove it entirely, including any surrounding bone tissue. However, in some cases, small pieces of the tooth or bone may break off and remain in the socket.
Unlock the Ultimate Dentistry eBook – Your Lifetime Guide to Dental Health!
Over time, these fragments may become covered by gum tissue but can still cause issues, such as pain or infection, if they are not properly addressed.
The formation of a bone spicule typically occurs due to incomplete healing of the extraction site. Factors that can contribute to the development of bone spicules include:
- Fragmented Tooth or Bone: During the extraction process, particularly if the tooth is impacted or fractured, fragments of the tooth or surrounding bone can break off and remain lodged in the socket.
- Poor Healing Response: Individuals with certain medical conditions like diabetes or compromised immune systems may experience delayed healing. This delay can prevent the extraction site from properly closing, allowing bone fragments to persist.
- Inadequate Post-Operative Care: Neglecting proper post-operative care instructions from the dentist, such as rinsing with saltwater, avoiding vigorous rinsing or sucking actions, and not following prescribed medications, can increase the likelihood of bone spicules forming.
The presence of a bone spicule can cause localized pain and irritation, especially when eating or brushing near the affected area. It’s essential to address these fragments promptly to prevent further complications.
In this blog post, we will delve into the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for bone spicules. Understanding these aspects will help you recognize the signs and know when to seek professional dental care for optimal oral health.
Causes of Bone Spicule
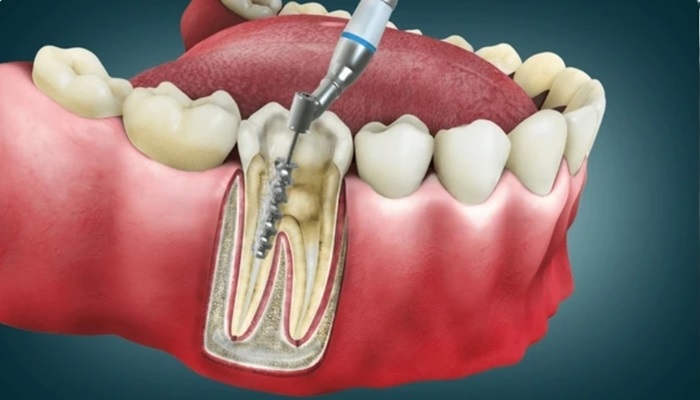
A bone spicule, also known as a retained root fragment, sequestrum, or dental bone spur, typically occurs following dental procedures such as tooth extractions. This condition arises when fragments of the tooth’s root or surrounding bone pieces remain embedded in the gum tissue after an extraction.
The primary cause is incomplete healing of the extraction socket, which allows these small fragments to protrude through the gum tissue and become exposed.
During a tooth extraction, it is common for pieces of the tooth or bone to break off and remain in the socket. Factors such as the complexity of the extraction, the condition of the tooth being removed (e.g., whether it was impacted or fractured), and the skill of the dentist performing the procedure can influence the likelihood of bone spicule formation. In some cases, a fragment of the tooth’s root may fracture and become displaced during extraction, contributing to the formation of a bone spicule.
Individuals with underlying health conditions that affect healing, such as diabetes, immunocompromised states, or mental disorders, are also at higher risk. These conditions can impair the body’s ability to heal properly, leading to delayed closure of the extraction site and increasing the chances of bone spicule development. Additionally, inadequate post-operative care, such as not following dentist-recommended guidelines for oral hygiene or failing to take prescribed medications, can further contribute to complications like bone spicules.
Understanding the causes of bone spicules is crucial for both dental professionals and patients. By addressing these factors, proper preventive measures can be taken during dental surgical procedures to minimize the occurrence of bone spicules and promote optimal healing of extraction sites.
Symptoms of Bone Spicule
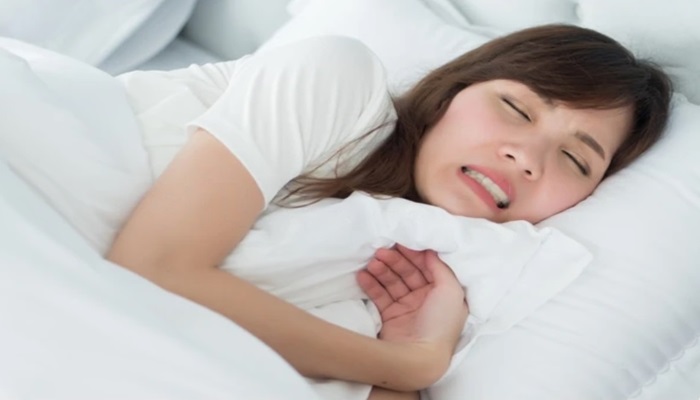
Bone spicules can manifest with several noticeable symptoms, primarily centered around discomfort and irritation in the affected area. Common symptoms include localized pain or tenderness, especially when chewing or applying pressure to the gum tissue near the extraction site. Patients may also experience sensitivity to hot or cold foods and beverages, as well as discomfort when brushing or flossing around the affected area. Persistent pain is another significant symptom that may require attention.
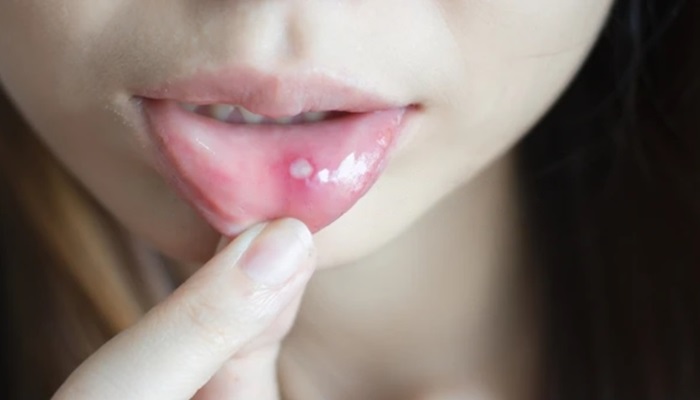
Another characteristic symptom of bone spicules is the presence of a small, sharp fragment protruding through the gum tissue. This fragment may be visible or palpable to the tongue, causing irritation or even injury to the surrounding soft tissues. In some cases, the gum tissue around the bone spicule may appear swollen, red, or inflamed, indicating an inflammatory response to the presence of the foreign body.
It’s essential to recognize these symptoms and seek prompt evaluation by a dental professional if bone spicule-related discomfort persists or worsens. Early intervention can prevent complications and ensure appropriate treatment to alleviate symptoms effectively. Over-the-counter pain relievers can help manage pain temporarily, but persistent pain or additional symptoms like shortness of breath warrant immediate professional attention.
Diagnosis of Bone Spicule
Diagnosing a bone spicule typically involves a thorough clinical examination by a dentist or oral surgeon. During the examination, the dentist will visually inspect the extraction site and palpate the surrounding gum tissue to identify any signs of inflammation, tenderness, or the presence of a protruding bone fragment.
In some cases, dental imaging techniques such as dental X-rays or cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) may be used to visualize the extraction site more clearly. X-rays can help confirm the presence and location of any retained root fragments or bone spicules that may not be visible during a visual examination alone.
Unlock the Ultimate Dentistry eBook – Your Lifetime Guide to Dental Health!
The diagnosis also includes evaluating the patient’s symptoms and medical history to understand the context of the bone spicule formation. Factors such as the complexity of the tooth extraction, any pre-existing dental conditions, and the patient’s overall health are considered during the diagnostic process. Additionally, the impact of the bone spicule on the patient’s daily activities and physical activities is taken into account.
Once diagnosed, the dental professional will discuss a treatment plan tailored to the specific case of the bone spicule, considering the severity of symptoms and the patient’s individual needs. This approach ensures that appropriate measures are taken to address the bone spicule effectively and promote optimal healing of the affected area, allowing the patient to resume normal physical and daily activities with minimal discomfort.
Treatment Options for Bone Spicule
Treatment for a bone spicule typically depends on its severity and impact on oral health. In many cases, if the spicule is small and causing minimal discomfort, no active treatment may be necessary as it can resolve on its own as the gum heals. However, when a bone spicule is symptomatic or causes irritation, several treatment options are available.
Water flossers, such as the Waterpik
Dentists may opt for conservative management, such as observing the spicule while ensuring good oral hygiene to prevent infection and irritation. In cases where the spicule is more problematic, extraction of the fragment under local anesthesia is a common approach.
This procedure involves carefully removing the spicule to relieve discomfort and promote healing. Antimicrobial mouth rinses or medications may also be prescribed to reduce inflammation and prevent infection post-extraction. Surgical intervention is rare but may be required for deeply embedded or inaccessible spicules. Follow-up care is crucial to monitor healing and address any complications that may arise.
Complications of Bone Spicule
While bone spicules are generally benign, they can lead to complications if not managed appropriately. The sharp edges of a spicule can irritate the surrounding gum tissue, causing pain, swelling, and inflammation. If bacteria accumulate around the spicule, it may lead to localized infection or dry socket, characterized by severe pain and delayed healing.
Interdental brushes are another excellent alternative
Delayed wound closure and persistent discomfort may occur if the spicule continues to irritate tissues or if there is incomplete removal. Rarely, chronic pain or sensitivity may develop, necessitating further treatment. Prompt dental evaluation is essential if symptoms persist or worsen after tooth extraction to prevent complications and ensure proper healing.
These paragraphs outline the treatment options available for bone spicules and potential complications associated with the condition, emphasizing the importance of timely intervention and comprehensive dental care.
Prevention of Bone Spicule
Preventing bone spicules involves several essential practices to minimize the risk of complications after tooth extraction. Firstly, it’s crucial to ensure that tooth extractions are performed by qualified dental professionals who can thoroughly remove the tooth and its roots.
This reduces the chances of leaving behind fragments that could potentially develop into bone spicules. Following extraction, adhering strictly to post-operative care instructions provided by the dentist is vital. This typically includes avoiding activities like vigorous rinsing or sucking motions that could disrupt the healing process and expose the bone.
Maintaining good oral hygiene practices is also key. Regular brushing with fluoride toothpaste, daily flossing, and using an antimicrobial mouthwash can help prevent infections that might complicate healing and lead to bone spicule formation.
Attending follow-up appointments as recommended by the dentist allows for monitoring the healing progress and early detection of any developing issues, such as the presence of bone spicules. Additionally, quitting smoking is strongly advised, as smoking delays healing and increases the likelihood of post-extraction complications.
A healthy diet rich in vitamins and minerals supports overall oral health and contributes to faster healing after dental procedures, reducing the risk of bone spicule formation. By incorporating these preventive measures, individuals can significantly reduce the chances of encountering bone spicules and promote optimal recovery following tooth extractions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while bone spicules can occasionally occur after dental procedures such as tooth extractions, they are largely preventable with proper dental care and adherence to post-operative guidelines. Ensuring extractions are performed by skilled professionals, following recommended post-operative care diligently, and maintaining excellent oral hygiene are crucial steps in minimizing the risk of bone spicule formation.
Unlock the Ultimate Dentistry eBook – Your Lifetime Guide to Dental Health!
Regular dental check-ups, cessation of smoking, and a nutritious diet further support the healing process and reduce complications. By prioritizing these preventive measures, individuals can enhance their oral health outcomes and mitigate the likelihood of encountering bone spicules after dental treatments.
At Grove Dental Clinic in Falls Church, VA, we’re dedicated to helping our patients achieve optimal oral health year-round.
Schedule your expert consultation at Grove Dental Clinic in Falls Church, VA today! Call (703) 578-0000 to book your appointment now!