Periodontal disease, commonly known as gum disease, is a significant oral health issue affecting millions of people worldwide. This condition involves the inflammation and infection of the gums, which can lead to severe dental problems if left untreated.
Periodontal disease is prevalent among adults and is a leading cause of tooth loss. Understanding periodontal disease is crucial for maintaining optimal oral health and preventing its serious consequences.
The term “periodontal” refers to the structures surrounding and supporting the teeth, including the gums, periodontal ligament, and alveolar bone. When these structures are compromised, it can result in periodontal disease, which progresses through several stages.
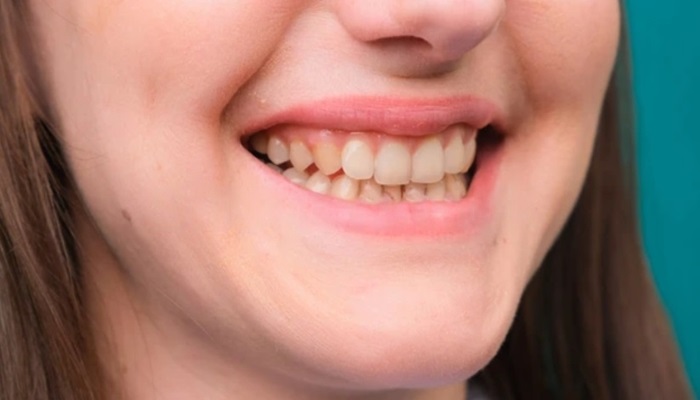
Early-stage periodontal disease, known as gingivitis, is characterized by red, swollen gums that may bleed during brushing or flossing. If untreated, gingivitis can advance to periodontitis, where the inflammation extends deeper into the tissues, causing the gums to pull away from the teeth, forming pockets that can become infected.
The prevalence of periodontal disease highlights the importance of awareness and early intervention. Studies show that nearly half of adults aged 30 and older in the United States have some form of periodontal disease.
The risk factors for developing this condition include poor oral hygiene, smoking, diabetes, and genetic susceptibility. By understanding these risk factors and recognizing the early signs of periodontal disease, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent its progression and maintain healthy gums and teeth.
By focusing on proper oral hygiene and regular dental check-ups, individuals can effectively manage and prevent periodontal disease, ensuring their smiles remain healthy and vibrant.
Causes of Periodontal Disease
Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is primarily caused by the accumulation of plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that forms on the teeth. While poor oral hygiene is a significant factor, there are various other causes and risk factors that can contribute to the development and progression of periodontal disease.
Understanding these causes is essential for preventing and managing this common dental condition. Inadequate brushing and flossing allow plaque to build up on the teeth and harden into tartar, which can only be removed by a dental professional. Plaque and tartar harbor bacteria that irritate and inflame the gums, leading to periodontal disease.
Some individuals are genetically predisposed to periodontal disease. Research indicates that genetics can account for up to 30% of the risk, making it important for those with a family history of gum disease to be extra vigilant about their oral care.
Smoking and the use of other tobacco products are significant risk factors for periodontal disease. Tobacco use impairs blood flow to the gums, reducing their ability to heal and making them more susceptible to infections. Smokers are more likely to develop periodontal disease and experience faster progression of the condition.
Hormonal fluctuations during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause can make gums more sensitive and prone to inflammation. This increased sensitivity can elevate the risk of developing periodontal disease. Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, can increase the risk of periodontal disease.
Diabetes impairs the body’s ability to process sugar, which can lead to higher levels of sugar in the saliva and promote bacterial growth. Other conditions that affect the immune system, like HIV/AIDS, can also increase susceptibility to periodontal disease.
Some medications can affect oral health by reducing saliva flow, leading to dry mouth, which increases the risk of gum disease. Other medications, such as certain anti-epileptic drugs and antihypertensives, can cause gum overgrowth, making it harder to maintain oral hygiene.
A diet lacking in essential nutrients can compromise the body’s immune response, making it harder to fight off infections, including those affecting the gums. A diet high in sugars and carbohydrates can also contribute to plaque buildup and periodontal disease.
Chronic stress can weaken the immune system, making it more difficult for the body to fight off infections, including periodontal infections. Stress can also lead to neglect of oral hygiene and unhealthy habits like smoking, further increasing the risk of gum disease.
By recognizing and addressing these causes, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent periodontal disease. Regular dental check-ups, good oral hygiene practices, a balanced diet, and avoiding tobacco can significantly reduce the risk of developing periodontal disease and help maintain healthy gums and teeth.
Symptoms of Periodontal Disease
Periodontal disease, a serious gum infection, can lead to various dental and health issues if not addressed promptly. Recognizing the symptoms early can help in managing and treating the condition effectively.
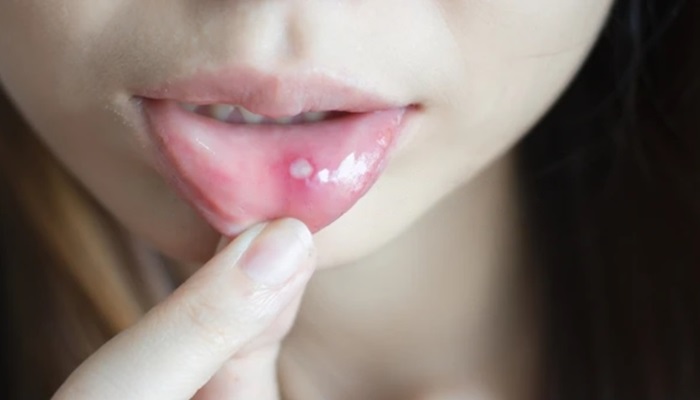
One of the earliest signs of periodontal disease is red, swollen gums. This inflammation occurs due to the body’s response to bacterial infection in the gum tissues. Healthy gums should be firm and pink, so any noticeable change in color or texture can be a warning sign.
Gums that bleed easily during brushing or flossing indicate periodontal issues. While occasional bleeding can happen, consistent bleeding is a symptom of gum disease. This bleeding results from the inflammation and irritation caused by plaque buildup along the gumline.
Chronic bad breath (halitosis) or a bad taste in the mouth can be a symptom of periodontal disease. The bacteria in plaque release toxins that cause an unpleasant odor and taste. Even after brushing and using mouthwash, the bad breath may persist if periodontal disease is present.
Gum recession, where the gums pull away from the teeth, exposing more of the tooth or its root, is a significant sign of advanced periodontal disease. This condition not only affects the appearance of the teeth but also increases sensitivity and the risk of decay.
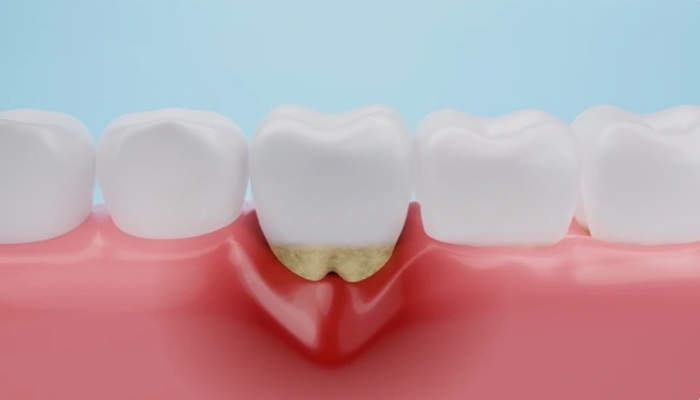
In periodontitis, the gums may begin to pull away from the teeth, forming pockets. These pockets become breeding grounds for bacteria and can lead to further infection. Dentists measure the depth of these pockets to assess the severity of periodontal disease.
As periodontal disease progresses, it can damage the supporting structures of the teeth, including the bones and connective tissues. This can result in teeth becoming loose or shifting from their original positions. If not treated, it can lead to tooth loss.
Pain or discomfort while chewing can be a symptom of periodontal disease. The infection and inflammation can make it difficult to bite or chew without experiencing pain. Increased tooth sensitivity to hot, cold, or sweet stimuli can indicate periodontal disease.
This sensitivity often results from receding gums and exposed tooth roots. Periodontal disease can cause changes in the way your teeth fit together when you bite. This can be due to the shifting of teeth or the weakening of the supporting structures.
By being aware of these symptoms and seeking prompt dental care, individuals can prevent the progression of periodontal disease. Regular dental check-ups and maintaining good oral hygiene are crucial in managing and treating periodontal disease effectively.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to consult with a dental professional to determine the appropriate treatment and care.
Diagnosis and Assessment
Periodontal disease, a serious condition affecting the gums and surrounding structures, requires thorough diagnosis and assessment by dental professionals. Early detection is crucial for effective treatment and management.
Patient medical and dental history is the starting point, with dentists reviewing risk factors such as smoking, diabetes, genetic predispositions, and other health conditions that could contribute to periodontal disease.
During a routine dental examination, the dentist or hygienist will visually inspect the gums for signs of periodontal disease, including redness, swelling, bleeding, gum recession, and the presence of plaque and tartar on the teeth.
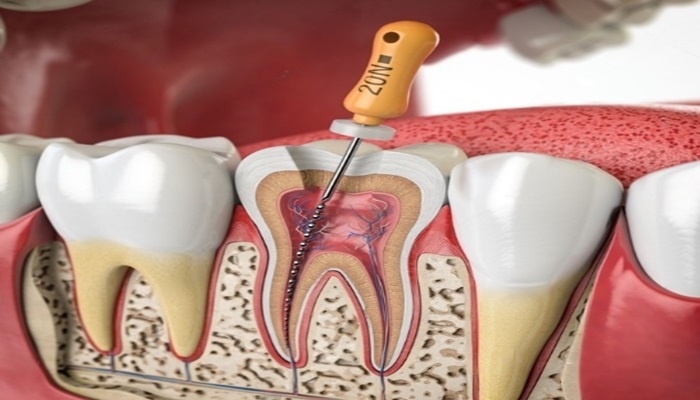
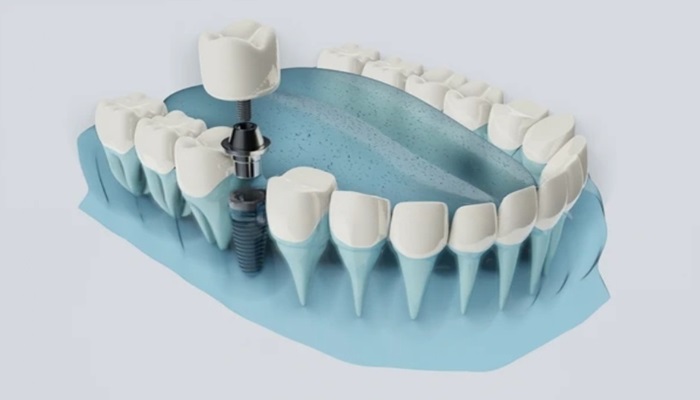
One of the key diagnostic tools is the periodontal probe, used to measure the depth of the pockets between the gums and teeth. Healthy gum pockets are usually 1-3 millimeters deep; pockets deeper than 4 millimeters may indicate periodontal disease. The dentist gently inserts the probe beside the tooth, beneath the gumline, to measure pocket depth at several points around each tooth.
Radiographic imaging, such as dental X-rays, is crucial for assessing the extent of periodontal disease. X-rays help visualize bone levels around the teeth, revealing bone loss that is not visible during a visual examination.
Dentists will also check for tooth mobility by gently rocking the teeth, as increased mobility can be a sign of severe periodontal disease, indicating loss of support from the surrounding bone and ligaments.
The color, texture, and overall condition of the gums are evaluated; healthy gums should be firm and pink, while gums affected by periodontal disease may appear red, swollen, and bleed easily.
Analyzing the patient’s bite can reveal changes caused by shifting teeth due to periodontal disease, helping in assessing the functional impact of the disease and planning necessary corrective treatments. The dentist will assess the amount and location of plaque and tartar buildup on the teeth, as these deposits harbor bacteria that cause periodontal disease, playing a critical role in the disease’s development and progression.
In some cases, dentists may take samples of plaque or tissue from the gum pockets to identify the specific bacteria causing the infection, which can help in tailoring antibiotic treatments for more effective results. By employing these diagnostic and assessment techniques, dental professionals can accurately determine the presence and severity of periodontal disease.
Early diagnosis is vital for preventing the progression of the disease and implementing effective treatment plans. Regular dental check-ups and prompt attention to any signs of periodontal disease are essential for maintaining optimal oral health. If you suspect you have periodontal disease, consult with a dental professional for a thorough evaluation and appropriate care.
Treatment Options for Periodontal Disease
Periodontal disease, a serious gum infection that damages the soft tissue and bone supporting the teeth, requires prompt and effective treatment to prevent further complications. There are several treatment options available, depending on the severity of the disease. Scaling and root planing is the first line of defense against periodontal disease.
Scaling involves removing plaque and tartar from the tooth surfaces and beneath the gums. Root planing smooths the root surfaces, discouraging further buildup of tartar and bacteria. This deep cleaning procedure helps the gums reattach to the teeth, reducing pocket depth and improving gum health.
To control bacterial infection, dentists may prescribe topical or oral antibiotics. Topical antibiotics can include mouth rinses or gels inserted into the periodontal pockets after scaling and root planing. Oral antibiotics may be used for more extensive infections.
This therapy helps to reduce bacterial colonies and inflammation. In cases where non-surgical treatments are insufficient, periodontal surgery may be necessary. There are several types of surgical procedures. Flap surgery, or pocket reduction surgery, involves lifting the gums back to remove tartar deposits and smoothing the irregular surfaces of the damaged bone. Bone grafting involves replacing or encouraging new bone growth in areas destroyed by periodontal disease.
Soft tissue grafts use tissue taken from the roof of the mouth or another donor source to cover exposed roots, reduce gum recession, and improve the aesthetics and function of the gums. Guided tissue regeneration involves placing a small piece of mesh-like material between the bone and gum tissue to prevent the gum from growing into the bone area, allowing the bone and connective tissue to regrow.
Lasers can be used to remove inflamed gum tissue and bacteria around the roots of the teeth. Laser therapy can reduce bleeding, swelling, and discomfort compared to traditional surgical methods. It’s important to ensure the dental professional is trained and experienced in using this technology.
After the initial treatment of periodontal disease, regular maintenance therapy is crucial. This typically involves more frequent dental cleanings, every three to four months, to keep periodontal disease under control. Maintenance therapy helps prevent the recurrence of the disease and maintains the health of the gums and teeth.
Effective treatment of periodontal disease also includes proper home care and lifestyle changes. Good oral hygiene, such as brushing twice a day with fluoride toothpaste, flossing daily, and using an antiseptic mouthwash, can help control plaque buildup. A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals supports gum health and helps prevent periodontal disease. Smoking is a significant risk factor for periodontal disease, and quitting smoking can improve treatment outcomes and overall oral health.
By employing these treatment options, dental professionals can effectively manage periodontal disease, restoring oral health and preventing further complications. Regular dental check-ups and good oral hygiene practices are essential for maintaining the benefits of treatment and ensuring long-term periodontal health. If you suspect you have periodontal disease, consult with a dental professional to determine the best treatment plan for your needs.
Prevention and Maintenance
Preventing periodontal disease is crucial for maintaining healthy gums and teeth. Implementing effective preventive measures and maintaining good oral hygiene can significantly reduce the risk of developing this serious dental condition. Brushing your teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and using a soft-bristled toothbrush can gently clean all surfaces of your teeth and gums.
Electric toothbrushes can also be highly effective in removing plaque. Flossing daily to remove plaque and food particles from between your teeth and under the gumline is essential for reaching areas that a toothbrush cannot. Using an antiseptic mouthwash can further reduce plaque and bacteria in the mouth, helping to prevent periodontal disease.
Regular dental check-ups are also important. Visiting your dentist at least twice a year for professional cleanings removes tartar that cannot be removed by regular brushing and flossing. Regular dental exams help in the early detection of periodontal disease and other dental issues, allowing for timely intervention.
Consuming a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, such as calcium and vitamin D, is essential for maintaining healthy teeth and gums. Foods like dairy products, leafy greens, and nuts are particularly beneficial. Reducing the intake of sugary snacks and beverages can help prevent plaque buildup and reduce the risk of periodontal disease.
Quitting smoking can significantly improve your gum health and enhance the effectiveness of periodontal treatments. Chronic stress can weaken the immune system, making it harder for the body to fight off infections, including those that affect the gums.
Engage in stress-reducing activities such as exercise, meditation, and hobbies. Drinking plenty of water throughout the day helps wash away food particles and bacteria, reducing the risk of plaque buildup. Fluoridated water can also help strengthen tooth enamel and prevent decay.
Using interdental brushes or dental picks to clean between teeth where a regular toothbrush might not reach is especially helpful for individuals with braces or other dental appliances. Cleaning your tongue with a tongue scraper can help reduce bacteria in the mouth and improve overall oral hygiene.
Educating yourself about periodontal disease and its risk factors can motivate better dental care practices. Adhering to the personalized dental care plan provided by your dentist, which may include specific instructions for brushing, flossing, and using certain dental products tailored to your needs, is also crucial.
By incorporating these preventive measures and maintenance tips into your daily routine, you can significantly reduce the risk of developing periodontal disease. Regular dental visits and a proactive approach to oral health are essential for maintaining strong, healthy gums and teeth. If you have any concerns about your periodontal health, consult with a dental professional for personalized advice and treatment options.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding and addressing periodontal disease is crucial for maintaining overall oral health. Periodontal disease, if left untreated, can lead to severe dental issues, including tooth loss and bone deterioration.
By recognizing the causes and symptoms early, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent and manage this condition effectively. Regular dental check-ups, good oral hygiene practices, and a healthy lifestyle are essential in preventing the onset and progression of periodontal disease.
Early diagnosis and intervention are vital in managing periodontal disease. Dental professionals employ various diagnostic tools and techniques to assess the health of your gums and provide tailored treatment plans. From scaling and root planing to surgical interventions and antibiotic therapies, there are multiple treatment options available to restore periodontal health.
Prevention and maintenance are the cornerstones of periodontal care. Consistent oral hygiene routines, regular professional cleanings, a balanced diet, and avoiding tobacco products are key strategies in maintaining healthy gums and teeth. Educating yourself about periodontal disease and following your dentist’s advice can significantly reduce the risk of developing this condition.
By addressing periodontal disease early and maintaining good oral hygiene, you can ensure a healthy, vibrant smile. Regular dental visits and a proactive approach to oral health will help you avoid the severe consequences of periodontal disease and enhance your overall well-being.
If you suspect any signs of periodontal disease, consult with a dental professional promptly to receive appropriate care and treatment. Remember, healthy gums are the foundation of a healthy smile, and taking care of your periodontal health is an investment in your long-term dental health.
At Grove Dental Clinic in Falls Church, VA, we’re dedicated to helping our patients achieve optimal oral health year-round.
Schedule your expert consultation at Grove Dental Clinic in Falls Church, VA today! Call (703) 578-0000 to book your appointment now!