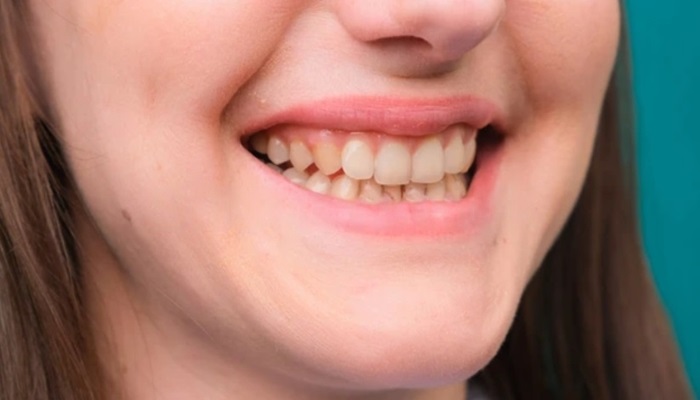
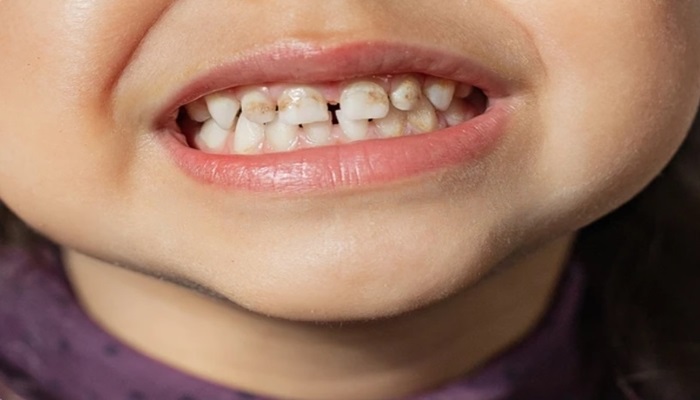
Dark spots on teeth that aren’t cavities can be a source of concern for many individuals. These discolorations, while not indicative of tooth decay, can affect the appearance of one’s smile and raise questions about overall dental health. Unlike cavities, which result from the breakdown of tooth enamel due to bacterial activity, these dark spots are caused by a variety of other factors. Understanding the reasons behind these dark spots is essential for anyone looking to maintain a bright and healthy smile.
Dark spots on teeth can be caused by external and internal factors. External factors include staining from foods and beverages like coffee, tea, red wine, and dark-colored fruits. Tobacco use, whether through smoking or chewing, can also lead to significant discoloration. Internal factors might include conditions like fluorosis, which occurs due to excessive fluoride exposure during tooth development, and certain medications that can cause intrinsic stains. Additionally, genetic factors and trauma to the teeth can result in dark spots.
Dental Herb Company – Tooth & Gums Tonic
Addressing these spots involves not only identifying and mitigating the underlying causes but also exploring various treatment options. This can range from professional dental cleaning and whitening treatments to lifestyle changes that prevent further staining. By understanding and managing the factors contributing to dark spots on teeth, individuals can maintain better oral health and enjoy a more aesthetically pleasing smile.
What Are Dark Spots on Teeth?
Dark spots on teeth that aren’t cavities are areas of discoloration on the tooth surface that can range in color from light brown to black. Unlike cavities, which are caused by bacterial decay leading to the demineralization of tooth enamel, these spots result from other factors. Understanding what these dark spots are and how they differ from cavities is crucial for proper dental care and treatment.
One common cause of dark spots is extrinsic staining, which occurs on the outer layer of the tooth (the enamel). This type of staining is often due to the consumption of certain foods and beverages, such as coffee, tea, red wine, and dark berries, which contain chromogens that stick to the enamel. Additionally, sugary foods and tobacco use, whether smoking or chewing, can lead to significant extrinsic staining due to the presence of tar and nicotine. These substances not only stain the teeth but also create a sticky residue that makes it easier for stains to adhere to the enamel.
Intrinsic staining, on the other hand, occurs within the tooth and can be caused by various factors. Fluorosis, which results from excessive fluoride exposure during tooth development, can cause white or brown spots on the teeth. Certain medications, such as tetracycline antibiotics taken during childhood, can also cause intrinsic discoloration. Trauma to the teeth, such as a fall or impact, can disrupt blood flow to the tooth, leading to dark spots as the tooth heals. Medical conditions can also contribute to intrinsic staining.
These black spots are not indicative of decay but can still impact dental aesthetics and, in some cases, dental health. Proper diagnosis by a dental professional is essential to determine the exact cause of the discoloration and to develop an appropriate treatment plan. Treatments can range from professional cleanings and whitening procedures to more involved restorative techniques like bonding or veneers, depending on the severity and cause of the dark spots.
Common Causes
Dark spots on teeth that aren’t cavities can be alarming, but understanding their common causes can help in addressing and preventing them. These dark spots often result from external factors that lead to extrinsic staining of the tooth enamel.
One of the most prevalent causes is the consumption of certain foods and beverages that contain strong pigments. Coffee, tea, red wine, and dark-colored fruits like blueberries and cherries are known for their staining properties. These substances contain chromogens, which are pigment-producing compounds that easily adhere to the enamel, altering tooth color and causing dark spots. Regular consumption of these items without proper oral hygiene can lead to noticeable discoloration over time.
Tobacco use is another significant contributor to dark spots on teeth. Both smoking and chewing tobacco can cause severe staining due to the tar and nicotine present in tobacco products. These substances not only stain the enamel but also create a sticky residue that makes it easier for stains to cling to the teeth. Smokers often experience more pronounced discoloration, making tobacco cessation an essential step in preventing further brown stains.
Poor oral hygiene is a common cause of dark spots. Failing to brush and floss regularly allows plaque and tartar to build up on the teeth. Over time, this accumulation can harden and become difficult to remove, leading to dark spots. Regular dental cleanings and diligent home care routines are crucial in preventing these issues.
Certain medications can also contribute to the formation of dark spots on teeth. For example, some antibiotics, such as tetracycline, when taken during childhood, can cause intrinsic discoloration that manifests as dark spots. Additionally, some mouth rinses and toothpastes containing chlorhexidine or cetylpyridinium chloride can cause surface staining if used over long periods.
Understanding these common causes of dark spots on teeth that aren’t cavities is the first step in managing and preventing them. By being mindful of dietary habits, avoiding tobacco use, maintaining good oral hygiene, and being aware of the potential side effects of certain medications, individuals can reduce their risk of developing these unsightly discolorations. In cases where dark spots have already formed, treatments such as dental bonding can help restore the natural appearance of the teeth.
Less Common Causes
While dark spots on teeth that aren’t cavities are often due to common external factors, several less common causes can also lead to these discolorations. These causes are usually related to intrinsic factors or specific conditions affecting the teeth.
One less common cause is dental trauma. An injury to the tooth, such as a fall or impact, can damage the blood vessels and nerves inside the tooth. This can lead to internal bleeding within the tooth, which may result in a dark stain as the blood discolors the dentin. Over time, the discoloration can become more pronounced and may require dental intervention to address.
TheraBreath Healthy Gums Mouthwash Clean Mint
Genetic factors can also play a role in the formation of dark spots on teeth. Some individuals may be predisposed to enamel defects or other hereditary conditions that affect the appearance of their natural tooth. These genetic conditions can cause the enamel to be thinner or more porous, making it more susceptible to staining and discoloration.
Fluorosis is another less common cause of dark spots on teeth. This condition occurs when there is excessive exposure to fluoride during the developmental stages of the teeth. Fluorosis can cause white streaks, brown spots, or even pitted enamel, depending on the severity of the condition. While fluoride is beneficial in preventing cavities, overexposure can lead to these types of discoloration.
Certain systemic diseases and health conditions can also lead to dark spots on teeth. For example, metabolic disorders or conditions affecting the liver or kidneys can sometimes manifest as discolorations on the teeth. These spots are typically intrinsic and may require specialized dental treatments to manage.
Lastly, prolonged use of certain dental products can cause less common dark spots. Some antiseptic mouthwashes and toothpastes containing chlorhexidine or other strong antimicrobial agents can cause brown or black staining on the entire tooth. While these products are effective in controlling plaque and gingivitis, their staining potential is a side effect that needs to be considered.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing dark spots on teeth that aren’t cavities involves a comprehensive approach to accurately identify the underlying cause and determine the appropriate treatment. This process typically includes a combination of patient history, clinical examination, and diagnostic imaging.
The first step in the diagnosis is taking a detailed patient history. The dentist will ask questions about the patient’s dietary habits, tobacco use, oral hygiene practices, and any medications they are taking. This information helps in identifying potential external factors that might be contributing to the dark spots. Additionally, the dentist will inquire about any history of dental trauma or systemic health conditions that could be relevant.
A thorough clinical examination follows the patient history. During this examination, the dentist will visually inspect the teeth and gums, looking for signs of discoloration, staining, or other abnormalities. They will assess the location, size, and color of the dark spots to determine whether they are extrinsic or intrinsic. The dentist may also use dental instruments to check for surface roughness or irregularities that could indicate tartar buildup or other issues.
Diagnostic imaging is often necessary to provide a more detailed view of the teeth and underlying structures. Dental X-rays can help identify any internal discolorations and differentiate between cavities and non-cavity-related dark spots. X-rays can also reveal any hidden issues, such as trauma-related damage or developmental anomalies that might be causing the discoloration.
Oral-B Glide Pro-Health Dental Floss
In some cases, additional diagnostic tools, such as intraoral cameras or digital scanning devices, may be used to capture high-resolution images of the teeth. These tools allow the dentist to examine the teeth more closely and document the condition for further analysis.
Once the diagnosis is made, the dentist can develop a treatment plan tailored to the specific cause of the dark spots. This plan may include professional cleaning to remove extrinsic stains, whitening treatments for both extrinsic and intrinsic discoloration, or more advanced restorative procedures like bonding or veneers for severe cases. The dentist will also provide recommendations for preventing further discoloration, such as dietary changes, improved oral hygiene practices, or avoiding certain medications.
By combining patient history, clinical examination, and diagnostic imaging, dental professionals can accurately diagnose dark spots on teeth that aren’t cavities and offer effective treatment solutions to enhance their patients’ oral health and aesthetics.
Home Remedies
When it comes to addressing dark spots on teeth that aren’t cavities, several home remedies can help lighten or eliminate these discolorations. While professional dental treatments are often more effective, these home remedies can provide noticeable improvements, especially when used consistently over time.
One popular home remedy is brushing with baking soda. Baking soda is a mild abrasive that can help remove surface stains on teeth. To use, mix a small amount of baking soda with water to form a paste, and brush your teeth with it a few times a week. This can help reduce the appearance of dark spots caused by external staining agents like coffee, tea, and tobacco.
Another effective home remedy is oil pulling. This traditional Ayurvedic practice involves swishing a tablespoon of coconut oil in your mouth for about 15-20 minutes before spitting it out. Oil pulling is believed to remove toxins and reduce plaque buildup, which can contribute to dark spots on teeth. Regular oil pulling can help maintain a brighter, cleaner smile.
Using hydrogen peroxide as a mouthwash can also help lighten dark spots. Hydrogen peroxide is a natural bleaching agent and has antibacterial properties. To use, dilute hydrogen peroxide with an equal amount of water and swish it in your mouth for a minute or two before rinsing thoroughly with water. Be cautious with this method, as overuse can lead to tooth sensitivity.
Activated charcoal is another home remedy gaining popularity for its teeth-whitening effects. Activated charcoal can bind to surface stains and remove them from the enamel. To use, dip a wet toothbrush into activated charcoal powder and brush your teeth gently. Rinse thoroughly and follow up with regular brushing. This method should be used sparingly to avoid enamel wear.
Additionally, eating crunchy fruits and vegetables like apples, carrots, and celery can help scrub away surface stains due to their natural abrasiveness and high water content. These foods also stimulate saliva production, which helps wash away food particles and bacteria that can lead to discoloration.
While these home remedies can be effective in reducing dark spots on teeth that aren’t cavities, it’s essential to maintain good oral hygiene practices, including regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups, to ensure overall dental health and prevent future discolorations.
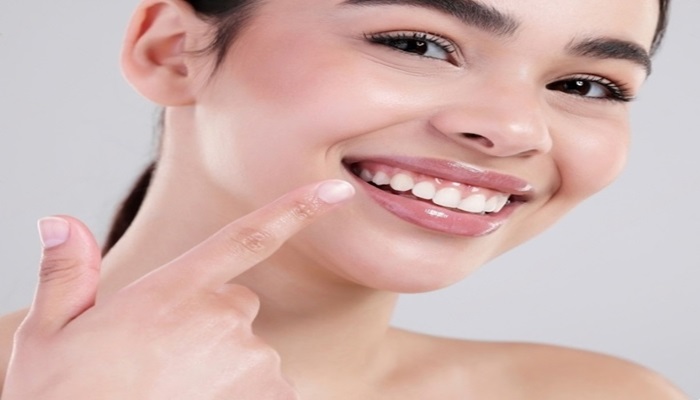

Prevention Tips
Preventing dark spots on teeth that aren’t cavities involves adopting a proactive approach to oral hygiene and making mindful lifestyle choices. By implementing these prevention tips, you can maintain a bright and healthy smile.
Firstly, maintaining excellent oral hygiene is paramount. Brush your teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste, and don’t forget to brush your tongue, as it can harbor bacteria that contribute to staining. Floss daily to remove plaque and food particles from between your teeth, where your toothbrush might not reach. Regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings are also crucial for preventing dark spots and ensuring overall dental health.
Limiting the consumption of staining foods and beverages can significantly reduce the risk of dark spots. Foods and drinks like coffee, tea, red wine, and dark berries are notorious for causing tooth discoloration. When you do consume these items, try to rinse your mouth with water afterward to minimize their staining effects. Using a straw for beverages like coffee and tea can also help reduce direct contact with your teeth.
Avoiding tobacco products is another critical prevention tip. Both smoking and chewing tobacco can lead to significant staining and other oral health issues. Quitting tobacco not only improves your overall health but also helps maintain a whiter, brighter smile.
Using a whitening toothpaste can help prevent dark spots by removing surface stains before they become more pronounced. Look for toothpaste with the American Dental Association (ADA) seal of approval to ensure it’s safe and effective.
Additionally, drinking plenty of water throughout the day helps wash away food particles and bacteria that can cause staining. Water also promotes saliva production, which naturally cleanses the teeth and neutralizes acids produced by bacteria.
Another preventive measure is being mindful of medications that might cause tooth discoloration. If you are prescribed a medication known to cause staining, discuss possible alternatives with your healthcare provider. If an alternative isn’t available, ensure you maintain rigorous oral hygiene to mitigate the staining effects.
Lastly, consider professional dental treatments, such as sealants or fluoride treatments, which can protect the enamel and prevent dark spots. Your dentist can provide personalized recommendations based on your dental health needs.
By following these prevention tips, you can significantly reduce the risk of developing dark spots on teeth that aren’t cavities and enjoy a healthier, more aesthetically pleasing smile.
Conclusion
In conclusion, dark spots on teeth that aren’t cavities are a common concern that can affect both the appearance and confidence of individuals. These spots can result from a variety of factors, including dietary habits, tobacco use, poor oral hygiene, certain medications, and even genetic predispositions. Understanding the causes of these dark spots is crucial for effective management and prevention.
Tom’s of Maine offers an anti-plaque flat floss
Home remedies, such as brushing with baking soda, oil pulling, using hydrogen peroxide mouthwash, and activated charcoal, can provide some relief from surface stains. However, it is important to use these remedies with caution and complement them with good oral hygiene practices to avoid potential side effects.
Preventing dark spots involves a proactive approach to dental care. Maintaining excellent oral hygiene, limiting the consumption of staining foods and beverages, avoiding tobacco, and staying hydrated are key strategies. Regular dental visits and professional cleanings are essential for preventing and managing dark spots effectively.
Ultimately, while dark spots on teeth that aren’t cavities may not pose the same risk as tooth decay, they can still impact one’s smile and self-esteem. By understanding the causes, exploring treatment options, and implementing preventive measures, individuals can achieve and maintain a bright, healthy smile. Prioritizing oral health and seeking professional advice when needed are essential steps in addressing and preventing these discolorations, ensuring overall dental well-being.
At Grove Dental Clinic in Falls Church, VA, we’re dedicated to helping our patients achieve optimal oral health year-round.
Schedule your expert consultation at Grove Dental Clinic in Falls Church, VA today! Call (703) 578-0000 to book your appointment now!