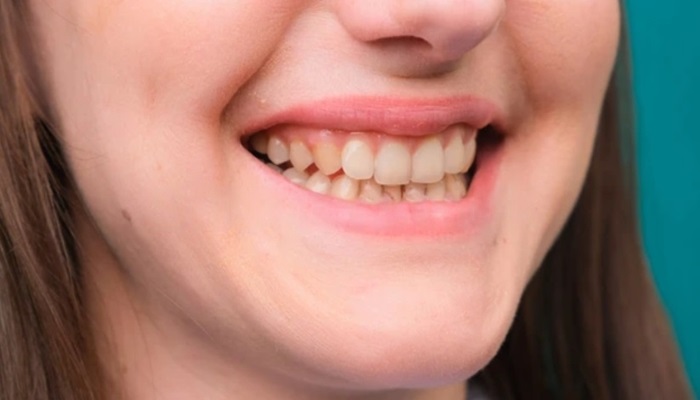
“Gums growing over teeth” refers to a condition where the gum tissue extends abnormally over the surface of the teeth, often covering a portion of the tooth or teeth entirely. This condition, known clinically as gingival overgrowth or gingival hyperplasia, can vary in severity and may lead to aesthetic concerns and oral health issues if left untreated.
The overgrowth of gums can occur due to various reasons, including poor oral hygiene habits, certain medications that stimulate gum tissue growth, and genetic predispositions. It can also be a symptom of underlying health conditions such as hormonal changes or systemic diseases.
Understanding the causes, symptoms, and potential treatments for gums growing over teeth is essential for maintaining oral health and preventing complications. This section explores the factors contributing to this condition and discusses effective strategies for managing and treating it. By addressing gums growing over teeth promptly, individuals can preserve both the function and appearance of their teeth and gums, promoting overall dental well-being.
Causes
“Gums growing over teeth,” medically termed as gingival overgrowth or gingival hyperplasia, can arise from various underlying factors. Understanding these causes is crucial for effectively managing and treating this condition.
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing can lead to plaque buildup along the gum line. Over time, this can irritate the gums, causing them to swell and potentially grow over the teeth.
- Medications: Certain medications, particularly ant seizure medications like phenytoin, immunosuppressant’s such as cyclosporine, and calcium channel blockers like nifedipine, are known to cause gingival overgrowth as a side effect. These medications can stimulate the growth of gum tissue, leading to the overgrowth observed.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, such as those occurring during puberty, pregnancy, or menopause, can increase blood flow to the gums and make them more sensitive to irritants like plaque and bacteria. This heightened sensitivity can contribute to gum tissue overgrowth.
- Genetic Predisposition: Some individuals may inherit genetic traits that predispose them to developing gingival overgrowth. Genetic factors can influence how gum tissue responds to various stimuli, including plaque and medications.
- Systemic Conditions: Certain systemic diseases, such as leukemia, diabetes, and Crohn’s disease, can affect gum health and contribute to gingival overgrowth. These conditions may alter immune responses or increase susceptibility to gum inflammation and overgrowth.
- Dental Appliances: Ill-fitting dental appliances, such as braces or dentures that constantly irritate the gums can lead to localized gingival overgrowth in response to chronic irritation.
- Other Factors: Smoking and tobacco use can impair gum health and increase the risk of gingival overgrowth. Additionally, poor nutrition and vitamin deficiencies, particularly deficiencies in vitamin C, may also play a role in gum tissue health and growth.
Dental Herb Company – Tooth & Gums Tonic
By understanding these underlying causes of gums growing over teeth, individuals and healthcare providers can identify contributing factors early and implement appropriate preventive measures or treatments to manage the condition effectively. Early intervention is crucial in preventing complications and maintaining optimal oral health.
Symptoms
Gums growing over teeth, clinically known as gingival overgrowth or gingival hyperplasia, manifest with noticeable symptoms that vary in severity. Typically, affected individuals may observe their gum tissue becoming enlarged and extending over the teeth, altering their normal appearance.
The gums may appear swollen, red, and tender, often bleeding easily, especially during brushing or flossing. Changes in gum texture, such as increased thickness or a spongy feel, can also accompany this condition. Some individuals may experience discomfort or pain, particularly when pressure is applied to the affected gums.
Difficulty in cleaning the teeth thoroughly due to the overgrowth can lead to plaque buildup and increase the risk of gum disease. In more severe cases, where the gums extensively cover the teeth, individuals may face challenges in speaking or chewing properly, impacting their daily activities and oral health.
Recognizing these symptoms early is crucial for seeking timely dental evaluation and appropriate treatment to manage the condition effectively and prevent further complications.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing gums growing over teeth involves a comprehensive assessment conducted by a dental or periodontal specialist. The diagnosis begins with a detailed clinical examination, where the dentist visually inspects the gums and teeth to evaluate the extent of gum overgrowth. They look for signs such as swelling, redness, and changes in gum texture.
A thorough review of the patient’s medical history, including medications taken, helps identify potential causes of gingival overgrowth, such as certain medications known to induce gum tissue growth. Periodontal probing is performed to measure the depth of the pockets between the gums and teeth, providing insights into the presence of gum disease or excessive gum tissue.
Dental X-rays may be taken to assess the underlying bone structure and detect any underlying issues contributing to the condition. In some cases, a biopsy of the affected gum tissue may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other possible causes.
Plaque/Tartar Remover for Teeth
Once diagnosed, the dentist discusses appropriate treatment options tailored to the individual’s needs, emphasizing the importance of early intervention to prevent complications and preserve oral health.
Treatment Options
Addressing gums growing over teeth, clinically termed gingival overgrowth or gingival hyperplasia, involves several treatment approaches tailored to the severity and underlying causes of the condition. For mild cases attributed to poor oral hygiene, enhancing daily brushing and flossing routines can mitigate plaque buildup and reduce gum inflammation.
Adjusting medications that contribute to gum tissue enlargement, such as ant seizure drugs or calcium channel blockers, under medical supervision may alleviate symptoms effectively. Professional dental cleanings performed by a dental hygienist or dentist are essential for removing hardened plaque (tartar) and maintaining gum health.
TheraBreath Healthy Gums Mouthwash Clean Mint
In cases where gum overgrowth is more pronounced, periodontal therapy such as scaling and root planning may be recommended to deep-clean below the gumline and reduce pocket depths. Surgical interventions like gingivectomy (surgical removal of excess gum tissue) or flap surgery (repositioning of gum tissue) may be necessary for severe instances where non-surgical methods prove inadequate.
Laser therapy represents an advanced option for reshaping gum tissue with minimal discomfort and faster recovery times compared to traditional surgery. Continuous monitoring and regular dental check-ups are critical to assess treatment effectiveness and maintain optimal gum health over time.
Prevention Tips
Preventing gums from growing over teeth, a condition known as gingival overgrowth or gingival hyperplasia, involves proactive oral hygiene practices and lifestyle choices to minimize risk factors. Here are essential prevention tips:
- Maintain Optimal Oral Hygiene: Brush your teeth at least twice daily with fluoride toothpaste and floss regularly to remove plaque and prevent gum irritation.
- Monitor Medication Use: If taking medications known to cause gum overgrowth, discuss potential alternatives or dosage adjustments with your healthcare provider to minimize adverse effects on gum health.
- Regular Dental Visits: Schedule routine dental check-ups every six months or as recommended by your dentist for professional cleanings and early detection of gum health issues.
- Quit Smoking: Avoid tobacco products, as smoking can impair gum health and increase the risk of gum disease and tissue overgrowth.
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Consume a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins to support overall oral and immune system health. Adequate vitamin C intake helps maintain healthy gum tissue.
- Manage Systemic Health: Control underlying health conditions such as diabetes through proper management and regular medical care to reduce the risk of gum complications.
By incorporating these preventive measures into your daily routine and seeking timely dental care, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of experiencing gums growing over teeth and promote long-term oral health.
Impact on Oral Health
Gums growing over teeth, clinically known as gingival overgrowth or gingival hyperplasia, significantly impact oral health in several ways. This condition alters the natural gum-to-tooth ratio, creating deep pockets around the teeth that are difficult to clean effectively with regular brushing and flossing alone. Consequently, plaque and bacteria can accumulate in these areas, leading to increased risks of gum inflammation (gingivitis) and more severe periodontal disease (periodontitis).
The presence of excessive gum tissue also complicates oral hygiene practices, making it challenging to maintain optimal dental care and potentially resulting in persistent plaque buildup and tooth decay. Aesthetic concerns are common as visible gum overgrowth can affect the smile’s appearance, causing social discomfort and self-consciousness.
Moreover, functional impairments may arise, such as difficulty chewing or speaking properly, especially in severe cases where the overgrowth hinders normal tooth alignment and bite. Dental procedures like filling cavities or placing dental crowns may also become more complex and less effective due to the presence of excess gum tissue, requiring additional steps to manage the overgrowth before addressing other dental issues.
Beyond physical impacts, gums growing over teeth can affect psychological well-being, contributing to feelings of anxiety or reduced self-esteem related to oral appearance and functionality. Managing this condition promptly with appropriate dental care is crucial to mitigate these effects and preserve long-term oral health.
Conclusion
In conclusion, addressing gums growing over teeth, also known as gingival overgrowth or gingival hyperplasia, is essential for maintaining optimal oral health and overall well-being. This condition can have significant implications, ranging from increased risk of gum disease and dental complications to aesthetic concerns and functional impairments.
Oral-B Glide Pro-Health Dental Floss
Effective management strategies include improving oral hygiene practices, adjusting medications under medical supervision, and seeking professional dental care for periodontal treatments or surgical interventions when necessary. Prevention plays a crucial role in mitigating the onset and severity of gum overgrowth, emphasizing the importance of regular dental check-ups, quitting smoking, and maintaining a balanced diet.
Early diagnosis and intervention are key to preventing complications and preserving both the aesthetic appearance and functionality of the teeth and gums. By prioritizing dental health and seeking timely treatment, individuals can minimize the impact of gums growing over teeth on their oral health, enhance their quality of life, and ensure long-term dental wellness.
At Grove Dental Clinic in Falls Church, VA, we’re dedicated to helping our patients achieve optimal oral health year-round.
Schedule your expert consultation at Grove Dental Clinic in Falls Church, VA today! Call (703) 578-0000 to book your appointment now!