What is a dental abscess?
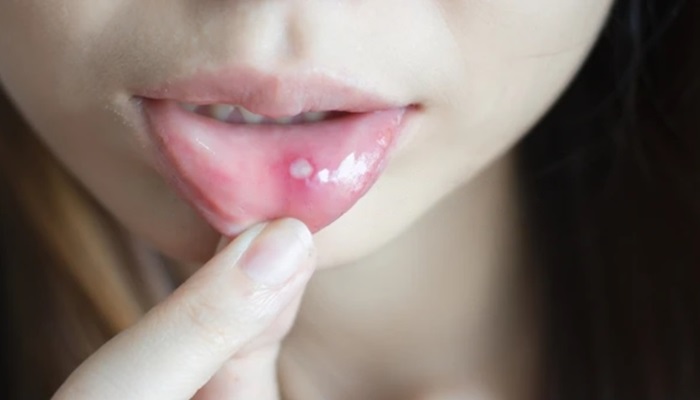
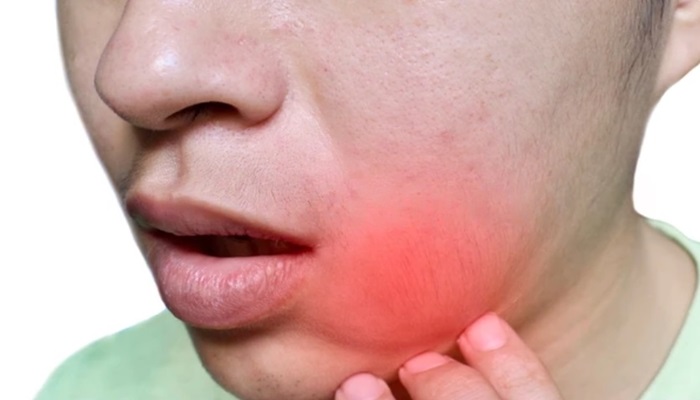
A dental abscess is a painful infection that occurs at the root of a tooth or in the gum tissue. It is typically caused by bacteria entering the tooth’s pulp, leading to inflammation, pus accumulation, and swelling. Dental abscesses can result from untreated tooth decay, gum disease, or dental trauma. They can vary in severity and may require prompt treatment to prevent complications and alleviate discomfort.
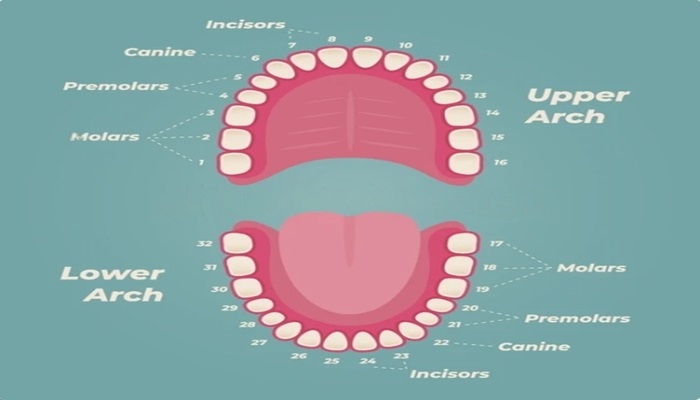
Types of dental abscesses (periapical, periodontal)
There are two main types of dental abscesses: periapical and periodontal. A periapical abscess occurs at the tip of a tooth’s root, usually as a result of untreated tooth decay or dental trauma. In contrast, a periodontal abscess forms in the gums, often due to advanced gum disease or a foreign object lodged in the gum tissue. Both types of abscesses can cause pain, swelling, and infection, and they require professional treatment to resolve.
Causes of dental abscesses
Dental abscesses are typically caused by bacterial infections that develop in the mouth. The primary factors contributing to abscess formation include untreated tooth decay, gum disease, dental trauma, and poor oral hygiene. When bacteria penetrate the tooth’s protective layers or enter the gum tissue through small openings, they can multiply rapidly, leading to inflammation and abscess formation.
Symptoms of dental abscesses
Dental abscesses often present with symptoms such as severe toothache, throbbing pain, swelling in the face or jaw, redness and tenderness in the affected area, fever, and difficulty chewing or swallowing. In some cases, a foul taste or odor may be present due to pus drainage from the abscess. Additionally, individuals with dental abscesses may experience sensitivity to hot or cold temperatures, swollen lymph nodes in the neck, and general malaise.
Complications of untreated dental abscesses
Untreated dental abscesses can lead to serious complications if left unchecked. Prolonged infection can spread to surrounding tissues, causing cellulitis, Ludwig’s angina, or even sepsis, which can be life-threatening. In severe cases, dental abscesses can lead to the formation of a dental fistula, a narrow tunnel that allows pus to drain from the abscess to the surface of the skin or into the mouth.
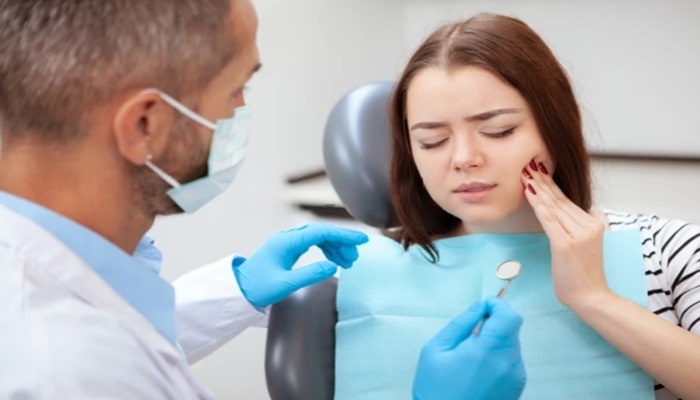
Diagnosis of dental abscesses
Diagnosing a dental abscess typically involves a thorough dental examination, including visual inspection, palpation of the affected area, and dental X-rays. During the examination, the dentist will look for signs of inflammation, swelling, and pus accumulation in the gums or around the affected tooth. Dental X-rays help visualize the extent of the infection, identify any underlying dental issues such as cavities or bone loss, and determine the appropriate course of treatment.
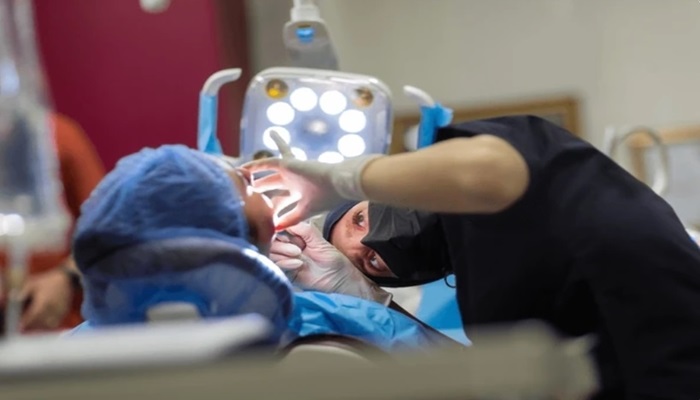
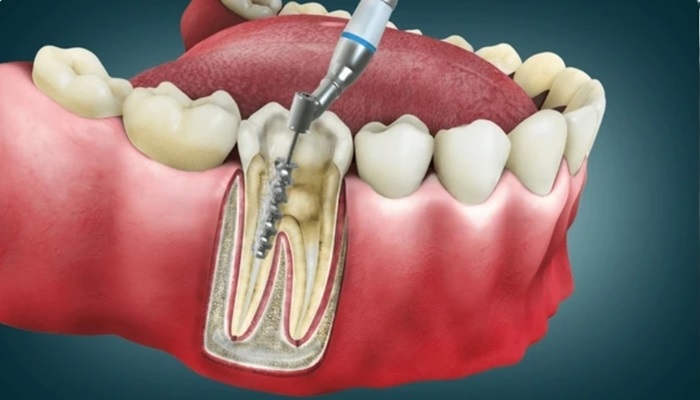
Dental abscess treatment options
Treatment for dental abscesses aims to eliminate the infection, alleviate pain and swelling, and prevent complications. The primary treatment options for dental abscesses include antibiotics, drainage procedures, and root canal therapy. Antibiotics are prescribed to kill the bacteria causing the infection and reduce inflammation. Drainage procedures, such as incision and drainage or root canal therapy, may be performed to remove pus from the abscess and alleviate pressure, which helps relieve pain and promote healing.
Home remedies for managing dental abscess symptoms
While professional dental care is essential for treating dental abscesses, several home remedies may help manage symptoms and promote healing. Rinsing the mouth with warm saltwater several times a day can help reduce inflammation and alleviate discomfort. Applying a cold compress to the affected area can help numb the pain and reduce swelling. Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen may also provide temporary relief from toothache and fever.
Preventive measures against dental abscesses
Preventing dental abscesses involves maintaining good oral hygiene practices and addressing risk factors that contribute to their development. Brushing teeth twice daily with fluoride toothpaste, flossing daily, and using an antimicrobial mouthwash can help remove plaque and bacteria from the mouth, reducing the risk of tooth decay and gum disease. Avoiding sugary and acidic foods and drinks can also help prevent cavities and protect tooth enamel.
Dental abscess in children: special considerations
Dental abscesses can occur in children, affecting their oral health and overall well-being. Common causes of dental abscesses in children include tooth decay, poor oral hygiene, and dental trauma. Children may experience symptoms such as tooth pain, swelling, fever, and difficulty eating or sleeping. Dental abscesses in children require prompt dental evaluation and treatment to prevent complications and alleviate discomfort.
Dental abscess during pregnancy: risks and management strategies
Dental abscesses during pregnancy pose risks to maternal and fetal health and require special considerations for management. Hormonal changes during pregnancy can increase the risk of gum disease and tooth decay, predisposing pregnant individuals to dental abscesses. Dental abscesses during pregnancy may also lead to complications such as preterm birth or low birth weight if left untreated.
Link between dental abscesses and systemic health issues
Dental abscesses are not only a localized dental problem but can also have systemic health implications if left untreated. Research has shown a link between dental abscesses and systemic conditions such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and respiratory infections. The bacteria responsible for dental abscesses can enter the bloodstream and spread to other parts of the body, contributing to inflammation and infection in distant organs and tissues.
Impact of poor oral hygiene on the development of dental abscesses
Poor oral hygiene is a significant risk factor for the development of dental abscesses. When plaque and bacteria accumulate on the teeth and gums due to inadequate brushing and flossing, they can lead to tooth decay, gum disease, and ultimately, dental abscesses. Additionally, poor oral hygiene habits such as skipping dental check-ups and neglecting to address dental issues promptly can allow dental problems to progress to abscess formation.
Dental abscesses in immunocompromised individuals
Immunocompromised individuals, such as those with HIV/AIDS, cancer undergoing chemotherapy, or organ transplant recipients taking immunosuppressive medications, are at increased risk of dental abscesses and associated complications. The weakened immune system in these individuals makes them more susceptible to infections, including dental abscesses, which can lead to serious systemic complications if left untreated.
Management of recurrent dental abscesses
Recurrent dental abscesses can be challenging to manage and may indicate underlying dental issues that require attention. Identifying and addressing the underlying cause of recurrent abscesses is crucial for preventing future episodes and preserving oral health. Dentists may recommend comprehensive dental evaluations, including X-rays and other diagnostic tests, to identify any contributing factors such as untreated tooth decay, gum disease, or dental trauma.
Surgical options for severe or recurrent dental abscesses
In cases of severe or recurrent dental abscesses that do not respond to conservative treatment, surgical intervention may be necessary to address the underlying issues and prevent further complications. Surgical options for severe or recurrent dental abscesses may include apicoectomy (surgical removal of the tooth’s root tip), incision and drainage procedures to remove pus and alleviate pressure, or dental extraction to remove the source of infection.
Long-term prognosis after dental abscess treatment
The long-term prognosis after dental abscess treatment depends on various factors, including the severity of the abscess, the effectiveness of treatment, and the patient’s overall oral health. In many cases, prompt and appropriate treatment can resolve dental abscesses and prevent recurrence, leading to a favorable long-term outcome. However, untreated or inadequately treated abscesses can result in complications such as tooth loss, bone damage, or systemic infection, which may impact the long-term prognosis.
Role of dentists and endodontists in managing dental abscesses
Dentists and endodontists play a crucial role in managing dental abscesses and providing appropriate treatment to patients. Dentists are trained to diagnose and treat various dental issues, including abscesses, through conservative or surgical interventions. Endodontists, who specialize in root canal therapy and other procedures involving the tooth’s pulp and surrounding tissues, may be consulted for complex or recurrent abscesses that require specialized care.
Importance of timely intervention in treating dental abscesses
Timely intervention is crucial in treating dental abscesses to prevent complications and promote successful outcomes. Delaying treatment for dental abscesses can allow the infection to spread, leading to severe pain, swelling, and systemic complications such as sepsis. Therefore, individuals experiencing symptoms of dental abscesses, such as severe toothache, swelling, or fever, should seek prompt dental evaluation and treatment to address the underlying infection and alleviate discomfort.
Dental abscesses and their impact on quality of life
Dental abscesses can have a significant impact on an individual’s quality of life, causing pain, discomfort, and functional limitations. Severe toothache, swelling, and difficulty eating or speaking can interfere with daily activities and affect overall well-being. Additionally, the psychological effects of dental abscesses, such as anxiety, embarrassment, and social withdrawal, can further diminish quality of life.
Dental abscesses: common misconceptions and myths
Despite being a common dental issue, dental abscesses are often surrounded by misconceptions and myths. One common myth is that dental abscesses will resolve on their own without treatment. In reality, dental abscesses require professional dental care to eliminate the infection and prevent complications. Another misconception is that draining the abscess at home is safe and effective. However, attempting to drain a dental abscess at home can lead to further infection, pain, and complications.
Dietary recommendations for preventing dental abscesses
Dietary habits play a significant role in oral health and can influence the risk of dental abscesses. Consuming a diet high in sugary and acidic foods and drinks can contribute to tooth decay and gum disease, increasing the risk of dental abscesses. Therefore, it’s important to limit the intake of sugary snacks, sodas, and acidic beverages and opt for nutritious foods that support oral health, such as fruits, vegetables, dairy products, and lean proteins.
Dental abscesses in elderly individuals: challenges and management strategies
Elderly individuals are at increased risk of dental abscesses due to age-related changes in oral health and underlying medical conditions. Common challenges in managing dental abscesses in elderly individuals include compromised immune function, reduced saliva production, and limited access to dental care. Additionally, age-related factors such as dry mouth, medication use, and cognitive decline can contribute to oral health issues and increase the risk of dental abscesses.
Dental abscesses and their association with dental trauma
Dental trauma, such as a cracked or fractured tooth, can increase the risk of dental abscesses by providing a pathway for bacteria to enter the tooth’s pulp and cause infection. Additionally, dental trauma can damage the tooth’s protective layers, making it more susceptible to decay and abscess formation. Common causes of dental trauma include falls, sports injuries, car accidents, and biting down on hard objects.
Emerging trends in dental abscess management
Advancements in dental technology and research have led to emerging trends in the management of dental abscesses, offering new approaches for diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. One such trend is the use of telemedicine and teledentistry to provide remote consultations and monitoring for patients with dental abscesses, increasing access to dental care, especially in underserved areas. Another trend is the development of minimally invasive techniques for treating dental abscesses, such as laser therapy and photodynamic therapy, which can effectively kill bacteria and promote tissue healing with less discomfort and faster recovery times. Additionally, researchers are exploring novel approaches for preventing dental abscesses, including probiotics, antimicrobial mouth rinses, and targeted therapies that disrupt bacterial biofilms.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding dental abscesses is essential for maintaining oral health and preventing complications associated with untreated infections. Dental abscesses can have significant consequences if left untreated, ranging from severe pain and swelling to systemic infections and tooth loss. Therefore, recognizing the signs and symptoms of dental abscesses, seeking prompt dental care, and following recommended treatments are crucial for addressing dental abscesses effectively and minimizing their impact on oral and overall health. By practicing good oral hygiene, attending regular dental check-ups, and adopting healthy lifestyle habits, individuals can reduce their risk of dental abscesses and enjoy a lifetime of healthy smiles.
At Grove Dental Clinic in Falls Church, VA, we’re dedicated to helping our patients achieve optimal oral health year-round.
Schedule your expert consultation at Grove Dental Clinic in Falls Church, VA today! Call (703) 578-0000 to book your appointment now!