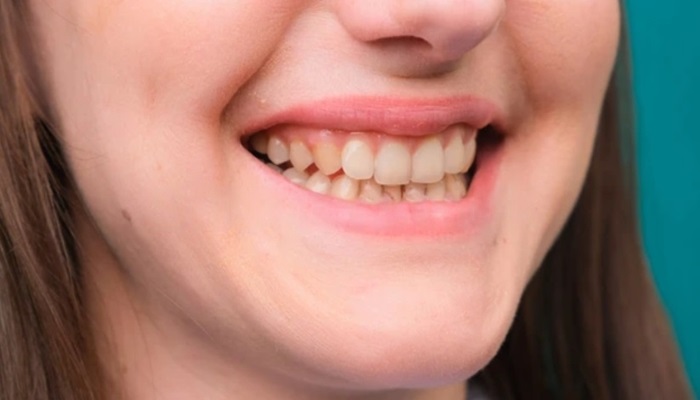
Understanding the stages of receding gums is crucial for anyone concerned about their oral health. Receding gums, a condition where gum tissue pulls away from the teeth, exposing tooth roots, progresses through several identifiable stages. Each stage presents unique challenges and treatment options, making early detection and intervention vital.
This guide aims to explore the various stages of receding gums comprehensively, from initial symptoms of inflammation to advanced recession, providing insights into causes, symptoms, prevention, and treatment strategies.
Best Smart Rechargeable Electric Power Toothbrush
By gaining a thorough understanding of these stages, individuals can better protect their gums, maintain dental health, and seek timely professional care when needed.
What are Receding Gums?
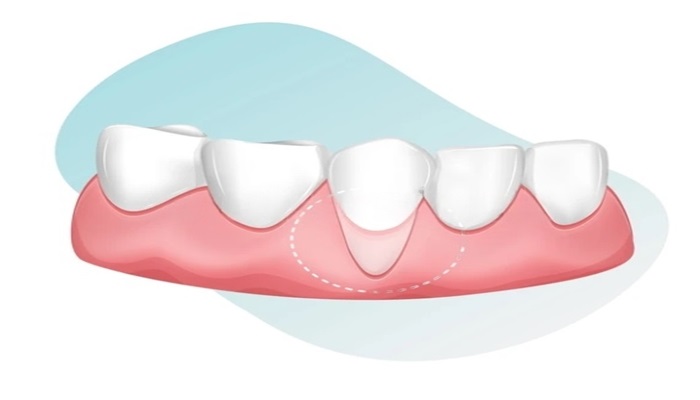
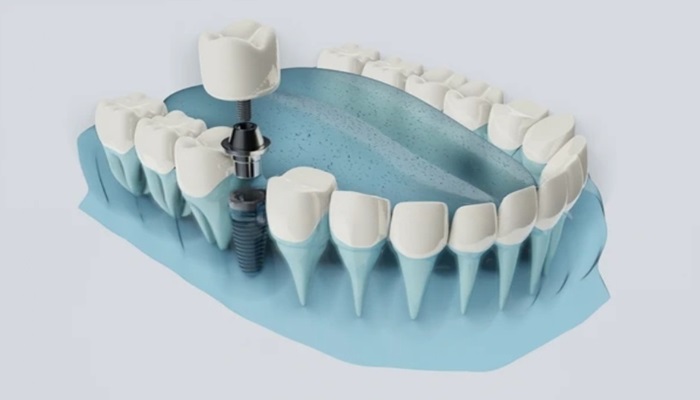
Receding gums stages involve the gradual erosion of gum tissue around the teeth, exposing more of the tooth surface and, in severe cases, the root. This condition typically progresses through several identifiable stages, each characterized by distinct symptoms and challenges.
Dental Herb Company – Tooth & Gums Tonic
Initially, receding gums may manifest as minor gum recession or inflammation, often overlooked until more noticeable symptoms arise. Common causes include poor oral hygiene practices, gum disease, aggressive brushing, and genetic predispositions. As the condition advances through moderate to severe stages, symptoms worsen, including increased tooth sensitivity, visible gum recession, and potential tooth mobility.
Understanding the early signs of receding gums and their progression is crucial for implementing preventive measures and seeking timely treatment from dental professionals to mitigate further damage and maintain oral health.
The Stages of Receding Gums: Stage 1: Initial Inflammation
In the receding gums stages, the initial inflammation stage is the first indication that something might be wrong with your gums. At this stage, the gums may appear slightly swollen and red, and you might experience mild discomfort.
This inflammation is usually caused by plaque buildup along the gumline, which harbors bacteria that irritate the gum tissue. If left untreated, this mild inflammation can progress to more severe stages of receding gums. It’s crucial to maintain good oral hygiene by brushing and flossing regularly and visiting your dentist for professional cleanings to address this initial stage effectively.
The Stages of Receding Gums: Stage 2: Early Recession
As we move to the second of the receding gums stages, early recession becomes more apparent. At this stage, you may notice that your gums are beginning to pull away from your teeth, causing increased tooth sensitivity, especially to hot and cold temperatures. The gum line starts to recede, exposing more of the tooth surface.
Common causes of early recession include gingivitis, tartar buildup, and aggressive brushing. Early intervention is key to preventing further damage. Improved oral care routines, such as gentle brushing with a soft-bristled toothbrush, flossing, and using an antimicrobial mouthwash, can help manage this stage.
Professional treatments, like scaling and root planing, may also be recommended by your dentist to remove tartar and smooth the root surfaces, promoting gum reattachment.
The Stages of Receding Gums: Stage 3: Moderate Recession
In the receding gums stages, moderate recession marks a significant progression of the condition. At this stage, the gums recede further, exposing a considerable portion of the tooth and its root. This can result in persistent sensitivity and discomfort, particularly when consuming hot, cold, or sweet foods and drinks.
The teeth may also start to appear longer due to the exposed roots. Common causes of moderate recession include untreated gingivitis, periodontitis, smoking, and hormonal changes.
Treatment for this stage often involves more intensive measures, such as deep cleaning (scaling and root planing), antibiotic therapy to reduce bacterial infection, and possibly laser treatment to promote tissue healing. It’s crucial to follow a strict oral hygiene regimen and visit your dentist regularly to monitor and manage the condition effectively.
The Stages of Receding Gums: Stage 4: Advanced Recession
Advanced recession represents the most severe of the receding gums stages. At this stage, the gums have receded significantly, leading to extensive tooth exposure and potential tooth loss. Symptoms include severe tooth sensitivity, noticeable gaps between teeth, loose teeth, and even pain.
Advanced recession is often caused by severe periodontitis, aggressive brushing, and lack of proper dental care over an extended period. Treatment options for this stage are more invasive and may include surgical procedures such as gum grafts, where tissue is taken from another part of the mouth and grafted onto the affected area, flap surgery to reduce the depth of the pockets, and regenerative procedures to restore lost bone and tissue. Managing advanced recession requires a comprehensive approach, including meticulous oral hygiene, professional dental treatments, and lifestyle changes to prevent further damage.
Diagnosis and Monitoring
Proper diagnosis and monitoring are essential in managing the receding gums stages. Early detection can prevent the condition from progressing to more severe stages. Dentists diagnose receding gums through a thorough examination of your oral cavity, which includes checking the gum line for recession, measuring the depth of periodontal pockets, and assessing the level of attachment of the gum tissue to the teeth. Diagnostic tools such as dental x-rays may be used to evaluate the bone levels around the teeth.
Regular dental check-ups are crucial for monitoring the condition. During these visits, your dentist will track changes in your gums, measure any further recession, and adjust treatment plans as necessary. Self-monitoring is also important; you should be aware of any changes in the appearance of your gums, increased tooth sensitivity, or discomfort. By staying vigilant and maintaining regular dental visits, you can effectively manage and treat the various stages of receding gums.
Prevention Tips
Preventing the progression of receding gums stages involves adopting a comprehensive oral care routine and making lifestyle changes that support gum health. Here are some key prevention tips:
- Proper Oral Hygiene: Brush your teeth at least twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush, using gentle, circular motions to avoid damaging the gum tissue. Floss daily to remove plaque and food particles from between the teeth and along the gumline.
- Regular Dental Visits: Schedule regular check-ups and cleanings with your dentist to monitor your gum health and catch any signs of recession early.
- Healthy Diet: Eat a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, particularly vitamin C, which is essential for gum health. Avoid sugary and acidic foods that can contribute to plaque buildup and gum disease.
- Avoid Tobacco: Smoking and using other tobacco products can significantly increase the risk of gum disease and gum recession. Quitting tobacco can greatly improve your oral health.
- Gentle Brushing Techniques: Avoid aggressive brushing, which can wear down the gum tissue. Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and gentle brushing techniques to clean your teeth effectively without harming your gums.
- Mouthguards: If you grind your teeth at night (bruxism), use a mouthguard to protect your teeth and gums from excessive pressure and wear.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to keep your mouth moist and help wash away food particles and bacteria.
By following these prevention tips, you can maintain healthy gums and prevent the progression of receding gums stages.
Treatment Options
Treating receding gums involves addressing the condition through a variety of methods tailored to the specific stage of progression:
- Non-Surgical Treatments:
- Scaling and Root Planing: This procedure cleans below the gumline to remove plaque and tartar buildup, helping to reduce inflammation and promote gum reattachment.
- Antibiotic Therapy: Used alongside scaling and root planing, antibiotics can target bacterial infection and prevent further damage to gum tissue.
- Surgical Treatments:
- Gum Grafting: In cases where gum recession is advanced, gum grafts are performed to cover exposed tooth roots with tissue taken from the palate or a donor source. This procedure helps to protect the roots from decay and sensitivity.
- Flap Surgery: This surgical technique involves lifting the gums to remove tartar deposits deep below the gumline. The gums are then repositioned to reduce pocket depth and facilitate healing.
- Regenerative Procedures:
- Guided Tissue Regeneration: This method stimulates the growth of new bone and tissue to replace what has been lost due to periodontal disease.
- Enamel Matrix Derivative (EMD): EMD is a regenerative material that can be applied to the root surfaces to encourage the regeneration of periodontal tissues.
- Laser Treatment:
- LANAP (Laser-Assisted New Attachment Procedure): This minimally invasive laser treatment targets diseased gum tissue while leaving healthy tissue intact, promoting gum reattachment and reducing pocket depth.
- Ongoing Maintenance:
- Good Oral Hygiene: Brushing with a soft-bristled toothbrush and flossing daily are essential to prevent plaque buildup and maintain gum health.
- Regular Dental Visits: Routine check-ups allow dentists to monitor the condition of your gums and provide timely interventions if necessary.
When to Seek Professional Help
Knowing when to seek professional help for receding gums is crucial to preventing further damage and preserving oral health:
- Persistent Symptoms: If you notice persistent symptoms such as gum recession, increased tooth sensitivity, or changes in the appearance of your gums (e.g., redness, swelling), it’s important to consult a dentist.
- Loose or Shifting Teeth: Teeth that feel loose or are shifting out of alignment could indicate advanced gum disease and require immediate attention.
- Bleeding Gums: Bleeding during brushing or flossing is not normal and could be a sign of gum disease.
- Pain or Discomfort: Any pain or discomfort in your gums or teeth should prompt a visit to the dentist for evaluation and treatment.
- Routine Check-Ups: Regular dental visits every six months allow your dentist to monitor the health of your gums and detect early signs of gum disease before they progress.
By seeking timely professional help and adhering to recommended treatment options, you can effectively manage receding gums and maintain optimal oral health.
Conclusion
Understanding the stages of receding gums is essential for maintaining optimal oral health and preventing further complications. From initial inflammation to advanced recession, each stage requires specific attention and appropriate treatment to halt progression and preserve gum tissue.
By practicing good oral hygiene, including regular brushing, flossing, and professional cleanings, you can mitigate the risk of plaque buildup and gum disease. Recognizing the signs of receding gums early, such as increased tooth sensitivity and visible gum recession, allows for prompt intervention and minimally invasive treatments like scaling and root planing.
For more severe cases, surgical options such as gum grafts and flap surgery can restore gum tissue and protect tooth roots. Remember, consistent monitoring and proactive dental care are key to managing receding gums stages effectively and maintaining a healthy smile for years to come.
At Grove Dental Clinic in Falls Church, VA, we’re dedicated to helping our patients achieve optimal oral health year-round.
Schedule your expert consultation at Grove Dental Clinic in Falls Church, VA today! Call (703) 578-0000 to book your appointment now!